Household Hazardous Waste: what a term! It’s a mouthful: three words that don’t really clarify what it encompasses. Add to that, city, hauler and marketing professionals like to shorten the term to HHW – which sounds even more mysterious. The EPA defines Household Hazardous Waste (HHW) as “leftover household products that can catch fire, react, or explode under certain circumstances, or that are corrosive or toxic.” Common HHW items include fluorescent bulbs, batteries, gasoline, household chemicals, pesticides, paints, antifreeze and asbestos…a real hodgpodge of toxic stuff.
At Gigantic, when tackling an HHW project, we start out thinking about our audience’s awareness of the problem. The problem with HHW is that it encompasses things as seemingly harmless as half-empty hair spray to those more easily perceived as dangerous, such as pesticides. When describing the hazards, we like the wording “toxic to you and/or the environment” to encompass all the potential negative outcomes.
Understanding HHW: Does It Matter?
When doing outreach, it’s important to describe the issue or item in question before you tell people what to do about it and give them a reason to dispose carefully. However, when considering HHW, we wonder, “do people really need to know the term?” Not necessarily. Communicating how HHW items should be handled can work either way:
- Explain the term and help people understand which items are considered HHW, then let them know how to safely dispose of it.
- Encourage use of a general “what goes where” app like StopWaste’s re:source tool that includes HHW items, without requiring the user to identify them as such. (IMAGE w link https://resource.stopwaste.org
Connect HHW Items with Real World Examples
It can also be helpful to put HHW disposal in context. When might residents be most likely to think about getting rid of HHW? Maybe before putting their house up for sale, when contemplating a spring cleaning or when tackling DIY house projects? Messaging that connects an activity with HHW items is more likely to be memorable.
Go Beyond the Carts
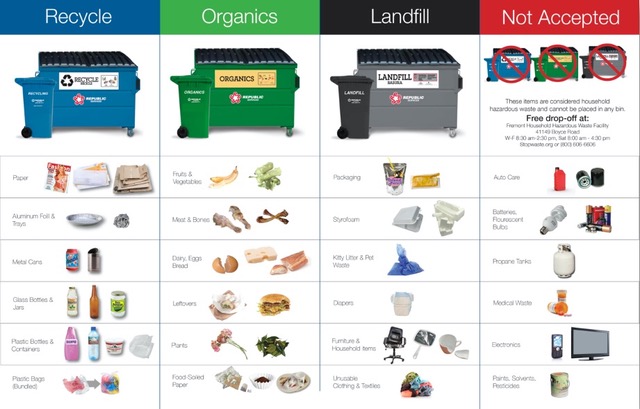
It could help if HHW items were called out more prominently in recycling guides as a category that needs different treatment, such as a “Not Accepted Curbside” or “Special Items” category.
Go for Impact
It also makes sense to focus on the HHW items that are most problematic in your area. Rather than implying the need to grasp a long list of items, focus on raising awareness about one item at a time, choosing those that would be most impactful if they were disposed of properly.
Thinking through the challenges and solutions of communicating about HHW before starting campaign design will save time and effort, while keeping people and nature safer.





 Our team has gotten even more Gigantic! We are pleased to announce the addition of Myer Venzon and Dennis Uyat to our team of Associates.
Our team has gotten even more Gigantic! We are pleased to announce the addition of Myer Venzon and Dennis Uyat to our team of Associates. Dennis holds a B.A. in Geography with a minor in Geospatial Information Science Technology from UC Berkeley and an A.A. in Recycling and Resource Management from Golden West College in Huntington Beach. They hold a certificates in Master Resource & Conservation and Master Compost & Solid Waste from the San Mateo County Office of Sustainability, and Zero Waste Community Associate by Zero Waste USA.
Dennis holds a B.A. in Geography with a minor in Geospatial Information Science Technology from UC Berkeley and an A.A. in Recycling and Resource Management from Golden West College in Huntington Beach. They hold a certificates in Master Resource & Conservation and Master Compost & Solid Waste from the San Mateo County Office of Sustainability, and Zero Waste Community Associate by Zero Waste USA.

 One of the challenges of zero waste outreach is how to convince people to NOT do something: buy new stuff. Every day Americans are bombarded by thousands of slick, seductive ads encouraging the purchase of shiny new things that they may or may not need. Helping the public to understand that “Reduce, Reuse, Recycle” is a list in priority of importance is tricky. How can reducing consumption be positioned as a positive?
One of the challenges of zero waste outreach is how to convince people to NOT do something: buy new stuff. Every day Americans are bombarded by thousands of slick, seductive ads encouraging the purchase of shiny new things that they may or may not need. Helping the public to understand that “Reduce, Reuse, Recycle” is a list in priority of importance is tricky. How can reducing consumption be positioned as a positive?

